Electric bikes, or e-bikes, have revolutionized the way we think about cycling, blending traditional pedal power with modern electric propulsion. In this blog, we'll explore exactly what is an e-bike, learn the mechanics of how these innovative machines work, and provide you with practical advice on choosing the right e-bike to suit your needs. Additionally, we'll highlight the numerous benefits that e-bike riding has to offer—from boosting fitness to contributing to environmental sustainability. Whether you're a commuting professional or a cycling enthusiast, understanding the world of e-bikes can enhance your riding experience and open up new avenues for personal and ecological advancement.

What Is an E-Bike?
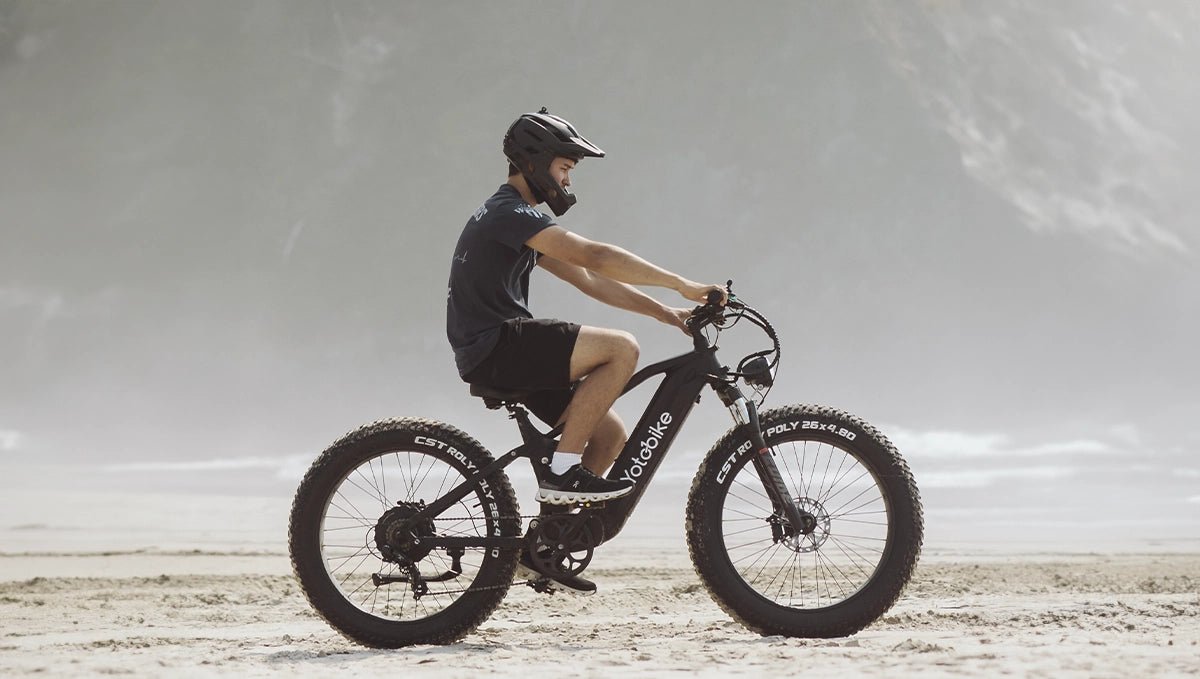
An electric bike, or e-bike, is a bicycle with an integrated electric motor designed to assist with pedaling. It resembles a conventional bike but has added components like a battery, a motor, and a control system. E-bikes are versatile and can be used for commuting, recreation, or even mountain biking. They offer a more accessible way to ride, allowing people to travel longer distances and tackle challenging terrains with ease.
How do Electric Bikes Work?
How do ebikes work? E-bikes work by using an electric motor to supplement your pedal power. When you pedal, the motor engages and provides additional assistance based on the level of power you select. Most e-bikes come with different levels of assistance, allowing you to adjust the boost to match your preference and riding conditions.
The key components of an e-bike are:
Motor: This is the heart of the e-bike, providing the power to drive it forward. Motors are typically located in the hub of the wheel or at the bike's crankshaft.
Battery: The battery powers the motor and is usually rechargeable. Battery life varies depending on the model, but a full charge generally allows for 20-100 miles of riding.
Controller: This device manages the motor's power output and allows you to adjust the level of assistance. It's typically mounted on the handlebars for easy access.
How to Choose the Right E-Bike
Selecting the right type of e-bike can be a game-changer for your cycling experience. It’s not just about choosing a bike; it’s about finding your perfect ride companion that matches your lifestyle and riding needs. With various types of e-bikes and assist levels available, understanding your options will help you make an informed decision.
Consider Your Riding Style
Before picking an e-bike, consider how you plan to use it. Are you commuting to work, riding for recreation, or tackling off-road trails? Your riding style will guide you toward the best e-bike type for your needs.
Commuters might prioritize a lightweight design, fast charging, and a comfortable ride.
Recreational riders may look for comfort, longer battery life, and versatile features.
Off-road enthusiasts typically need more durable frames and robust motor systems.
Understand the Classes of E-Bikes
In the United States, e-bikes are categorized into four classes based on their assistance levels and speed capabilities. Understanding these classes can help you determine which type aligns with your riding goals and legal requirements in your area.
Class 1 E-Bikes are pedal-assist only, with a maximum speed of 20 mph. These are ideal for city commuting and recreational use. They're typically allowed on bike lanes and most trails.
Class 2 E-Bikes have both pedal-assist and a throttle, with a maximum speed of 20 mph. This class is perfect if you prefer a bit of extra help when pedaling or want the option to ride without pedaling.
Class 3 E-Bikes are pedal-assist only, but with a higher speed limit of 28 mph. These are great for commuters who want to travel faster. However, they might not be allowed on all bike paths and trails.
Class 4 E-Bikes or electric motorcycles, exceed 28 mph and might not require pedaling. Due to their higher speeds, these are usually regulated more like motorcycles and may not be permitted on typical bike paths.
Evaluate the Motor and Battery
An e-bike's motor and battery play a significant role in its performance and range. Consider the motor's power, measured in watts, and the battery's capacity, measured in ampere-hours (Ah) or watt-hours (Wh). Higher wattage motors provide more power, while larger batteries offer extended range.
Mid-drive motors are balanced and efficient, making them a popular choice for Class 1 and Class 3 e-bikes.
Hub motors are typically found on Class 2 e-bikes and offer simplicity and reliability.
Assess the Frame and Design
The frame's design impacts comfort and durability. Choose a frame that suits your body type and riding style. Look for features like step-through frames for easy mounting or full-suspension for off-road stability.

Benefits of Riding an E-Bike
Riding an electric bike, offers a unique blend of efficiency, eco-friendliness, and enjoyment. Along with the many benefits, potential riders often ask, "Are electric bikes safe?" The answer is yes; with proper maintenance and adherence to traffic laws, e-bikes are as safe as traditional bicycles. Here are some key benefits of embracing this innovative mode of transportation:
- Enhanced Mobility:
E-bikes come equipped with electric motors that assist your pedaling, making it easier to cover longer distances and climb steep hills without excessive fatigue. This can significantly enhance your mobility, especially in urban settings where navigating traffic and road inclines can be challenging.
- Environmentally Friendly:
E-bikes are a green alternative to motor vehicles. They emit no pollutants and require less energy to operate than cars or motorcycles. By choosing an e-bike, you are contributing to reduced air pollution and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Health Benefits:
Despite the motor assistance, riding an e-bike is still an excellent form of exercise. It can improve cardiovascular health, build muscle tone, and boost overall physical fitness. Additionally, it's a low-impact activity that can be easier on your joints compared to traditional cycling.
- Cost-Effective:
E-bikes can be a cost-effective transportation option. They have lower maintenance costs than cars and don't require fuel, insurance, or high parking fees. The initial investment might be higher than for a traditional bike, but the long-term savings on transit fares, gas, and car maintenance can be substantial.
- Accessibility:
E-bikes level the playing field, providing an option for people of varying fitness levels and ages. They make cycling accessible to seniors, those recovering from injuries, or individuals who may not otherwise engage in regular physical activity due to physical limitations.
- Time Efficiency:
In many cities, e-bikes can be faster than cars during peak hours. They allow you to bypass traffic congestion, utilize cycling lanes, and take shortcuts that are not accessible to cars. This can lead to a more predictable and often shorter commute time.
- Fun and Recreational Opportunities:
E-bikes open up new opportunities for recreation and leisure activities. They allow riders to explore further distances and visit areas that might have been too challenging to reach with a regular bike. This can make outdoor activities more enjoyable and varied.
- Stress Reduction:
Riding an e-bike can also be a great way to reduce stress. The combination of physical activity, outdoor exposure, and the enjoyment of effortlessly cruising down the road can have significant mental health benefits.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the ins and outs of what is an ebike, delving into their mechanics, benefits, and the different types available. Whether you're considering an e-bike for efficiency, environmental benefits, or simply for the joy of riding, it's clear that e-bikes offer a versatile and sustainable alternative to traditional transport. As the popularity of electric bikes continues to grow, understanding how they work and what they offer can help you make an informed decision and potentially transform your daily commute or recreational activities.
FAQs
Here, we address some of the most common inquiries.
When was the first electric bike made?
The first electric bike was invented by Hossea W. Libbey of Boston in 1895. This early version was powered by a double electric motor within the hub of the crankset axle. This innovation marked the beginning of electric bicycles, although they did not become popular until advancements in battery technology occurred much later.
Are electric bikes good for the environment?
Electric bikes are generally good for the environment as they emit no direct pollutants and use less energy compared to cars. By replacing car trips, e-bikes reduce greenhouse gas emissions and traffic congestion.



























